A RACI chart is a way to identify your project teams’ roles and responsibilities for any project task, achievement, or delivery. By following the acronym RACI, you can clarify how responsibility is distributed and reduce confusion. It is a way of categorizing stakeholders to define their roles and responsibilities on a project. Mainly if you are operating a complex project with many decision-makers and many subject matter experts, with a RACI chart, you can avoid making poor decisions and avoid hurdles in the approval process that could affect the project’s overall success.
In 1984, three Norwegians, Kristoffer v. Grude, Tor Haug, and Erling S. Andersen, published the first version of the RACI chart for project management.
These charts are handy if participants can take on different roles throughout the project. For example, a participant has the role of being responsible for one delivery but has been informed about another. With a RACI chart, you can clearly describe these details and make sure everyone knows who is responsible for what.
You may have a different term for RACI chart. Some of the common alternate names of RACI chart are:
- RACI matrix
- Linear responsibility chart or LRC
- Responsibility Assignment Matrix or RAM
By following the acronym RACI, you can clarify how responsibility is distributed and reduce confusion. RACI means the following:
R-Responsible
This person is responsible for the entire work directly. There should only be one manager per task, so you know who to turn to if you have questions or updates. If a task has more than one person in charge, you lose clarity and confusion. Instead, try adding additional collaborators like some of the other roles on the RACI chart, which more than one person can fill.
A-Accountable
The accountable is in charge of overseeing the task’s overall completion, although they may not be the person doing the work. There are two ways to assign the accountable role:
- Sometimes the accountable is the project manager (or even the person in charge, although in that case, the person takes on two different roles during the task workflow). In these cases, the accountable must ensure that all work is done.
- In other cases, the accountable is a leader or senior executive who is in charge of approving the work before it is deemed complete. As in the case of the Lead role, there should only be one accountable.
C-Consulted
Consulted will be the person or persons who must review and approve the work before delivering it. There may be multiple respondents for each task, project achievement, or delivery. They are mostly the parties that provide the data based on either how the progress will impact the future work or their skillful domain on deliverable itself
I-Informed
Informed is the person or group of people who are informed regarding the job’s progress and completion. They are probably not involved in any other aspect of the delivery.
When and How to Use RACI Chart
Being clear about how project roles and responsibilities are assigned can help your team move quickly and reduce confusion about who is working on what. With a RACI chart, you can make sure you do not have two team members working on the same thing. As a result, it will be easier for you to collaborate with your team.
- RACI charts are handy when the decision-making process is divided between tasks.
- There may be scenarios in which the informed of one task or achievement is responsible, or the consulted of another.
- For tasks to have clearly defined, it is useful to track this work with a RACI chart.
- You have a high turnover rate on your staff and need to quickly onboard someone to a new job.
It’s not like all teams and projects are developed in the same way. It would help if you managed a team that communicates well and keeps up with their work, or your project may be small to take a moment to do this exercise stupidly. Do not think about taking the additional measure in situations like this.
The right way will be to categorize the following reasons in the decision or approval process that could help the project:
- If it includes high risk rather than general decisions that are capable of doing or reversing activities or tasks;
- If it involves high risk, not general decisions that can or can reverse a mission or operation;
- Related decisions that unnecessarily impede the operation by cross-cutting decisions from various classes;
- Low-risk actions are made personally or by a small team of others;
- Frequent low-risk ad hoc decisions are addressed rapidly at the work activists’ level themselves.
There is no need to buy sophisticated software; classic Word and Excel are more than enough to build and use a RACI chart. However, this functionality can be integrated into project management software suites.
The most common way to prepare a RACI chart is tabular, with the individuals (or groups) across the top and the list of tasks down the side. Following are some of the steps involved:
Determine project roles
Determine the different project roles assigned to the individual members: who does what, when, and how. Only one person must be assigned the roles of responsibility indicated by the abbreviations R and A. Having more than one person responsible for the same task increases the ambiguity and the possibility that the work is not carried out correctly. While this is the rule, having a single responsible person can lead to other kinds of problems.
If the responsible person is incompetent, for example, the whole process may not be done correctly. It is for this reason that there is often a hierarchy of responsible persons.
List down the project tasks
The second step is to make a list of assignments, milestones, and decisions that need to be made in the first left-hand column, from beginning to end. Identify and create a list of different project tasks. Use your work or task breakdown structure if you have one for speed.
Assign the RACI roles
Identify the people and their RACI roles. It is traditional to use roles instead of names on the chart but use actual names where it is only one person. Across the first row of each column, write the team members’ names or positions responsible for the assigned task.
Get aligned with your team
Consult your team and discuss their task with them so that you align with your team. It is not always possible to sit with the team and delegate the tasks assigned to each task when discussing. You must ensure that any individual assigned a position or duty agrees to and recognizes his role as agreed to and set out for him. This role assignment and interpretation of the task involved in assigning the role must be evident.
Implementation
To make sure that this practice of creating a RACI chart is useful, implement and work according to it. The RACI chart helps assign responsibilities to learn how to implement them. The secret to RACI success is balance. When there are insufficient or too many people in each position, task completion is prevented or slowed.
Rules of Using RACI Chart
The primary purpose of using a RACI chart is to increase efficiency, management, and productivity; to achieve it, we need to follow specific rules. Following are some of the rules that you need to follow while using a RACI chart:
Keep people informed
A RACI chart’s success depends on the fact that the individual members are well informed about their roles. Most of the time, you should not have to consult with participants; all you need to do is educate them. Ensure you have people in these positions, or you will run into issues, such as a lack of team coordination.
Do not do it in isolation-The RACI matrix is a management tool for good governance, but it is not a stand-alone system for modeling a management process as such. A RACI chart requires team coordination to perform different tasks in a project efficiently, so do not try to create a chart in isolation.
The right amount of people for a certain task
Another important rule for the beneficial use of the RACI chart is that you have the right amount of people for a specific task. If you add too many people to a task, it may become bulky. Too many people assigned to the same job will be a waste of money and time. So, if you have a short and straightforward task, the Accountable may also be Responsible.
Do not have too many consults-Ensure that there are too many consultants for a task. It avoids parallel or duplicate processes. If it is essential to define more than one person in charge, each one’s division of tasks must be clear and well defined. Having way too many consultations can cause the job to take longer to complete.
One accountable per task
Ensure that there is only one accountable for each task so that resources are appropriately managed without any drain. When more than one individual is working on a project, it is analogous to having one plane with multiple pilots. It does not work, but it is also impossible to shift the plane forward if there is no pilot.
Using a RACI on Agile Project
Agile handling and a clear view of the various actors’ responsibilities here are two essential elements for your projects’ success. Each manager, particularly the project manager, should define an overview of the roles to optimize tasks’ distribution and avoid wasting time. To address the various challenges of project management, the RACI proves to be an indispensable governance tool for companies that simplifies everything related to resource planning. You can use a RACI chart on an Agile project to evaluate the difference in Scrum effectively. It can be achieved by using a combination of RACI+F.
What is ‘F’
F is an acronym for Facilitator. Using it together with the RACI chart accounts for how Scrum is run and how roles can be delegated accordingly. However, this Facilitator function is best for the project’s Scrum Master or Project Manager, and therefore it brings another layer of additional detail to the chart. Even though many of the variations of RACI are present, some practitioners feel the need to add new tasks (such as “facilitator/coaching”), new activities and duties of Scrum (such as ensuring the consistent practice of Scrum throughout teams or removing obstacles) to the matrix, or new positions and roles (such as the “scrum team”).
RACI on agile project
Much of the Agile values inspire and communicate regularly with the team because those who ought to be contacted should not be informed that they are contributors. It’s thus not the case that each Agile project must use the RACI chart. Many tasks are tacit if you adopt an Agile approach like Scrum. Evaluate your needs before proceeding with a RACI. Several principles, ideas, and ideals are promoted by both the Agile and Scrum models that deviate from previous project management paradigms. We can show implicit obligations in Agile according to these values and principles. Though individual tasks are delegated to persons responsible for executing the tasks, the entire team has responsibility. With all these inputs into RACI Scrum-flavored, the RACI chart can be built by the PM/PO at the same launch meeting where the Scrum Team sends out the project definition of the project and can be discussed at long last.
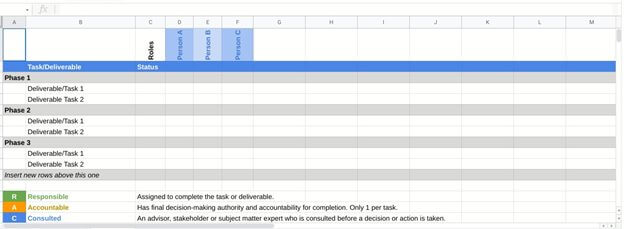
Create a RACI chart, make a list of all the tasks, accomplishments, or deliverables for your project. Then, identify which team members are responsible, approving, consulted, and informed for each item on that list.
Let us say you are updating the homepage of your website. Among the project participants are the following people:
- Creative writer
- Designer
- Website Admin
- Web developer
Suppose one wants to create a RACI chart for five tasks and submissions:
- Update your homepage calls to action (CTA).
- Update customer history on home page.
- Renew the website design.
- Improve the loading speed.
- Update the home page layout.
A RACI chart would look like this:
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
There are certain mistakes that may make the RACI chart less effective and it is necessary to avoid them. Below we have mentioned some of common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Add confusion- If you add too many tasks or assign too many tasks to a member, it may become bulky and add confusion. To avoid this from happening, add the necessary tasks.
Time-consuming to create- A common misconception regarding a RACI chart is that it is time-consuming; this may be if you are not doing it correctly. Also, you always have the option to use a template that makes the process smooth.
Ignored after approval- It happens when you have approved a task but have not further processed it. It can lead to confusion in the end. The best way to avoid it is by processing the task soon after they are approved.
Does not account for the approval process on the tasks- A common problem that people must face is that a RACI does not account for the tasks’ approval process; to avoid it, the project manager can handle this process.
Project manager as the catchall- The project manager may act as the catchall as he is responsible for assigning and approving tasks. However, this can be avoided by coordination and discussion among the team.
Confusing responsible and accountable- Another mistake that may happen is that the project manager may confuse responsible and accountable in a RACI chart. It can be avoided by adequately formulating and assigning distinct roles to both responsible and accountable.
The tension between consulted and informed- While using a RACI chart, tension may occur between consulted and informed. The project manager can avoid it by acting as a mediator.
Advantages of Using a RACI Chart
A RACI chart makes it clear how project roles and responsibilities should be assigned which makes the project management and your team more productive. There are also several other advantages of using a RACI chart, some of them are:
Streaming communication
Team members need to be able to communicate quickly and efficiently as part of a smooth-running activity. It is unnecessary to send hazy emails or make distressing phone calls at the last minute, which may lead to misunderstanding. Not only are team members easier to work with by using the project RACI chart, but they can also identify the correct person with a more serious complaint. While most businesses have an HR department to manage internal problems, having someone on hand enables team members to guide the appropriate individual. It reduces the likelihood of any problems lingering in the workplace.
Avoid overloading people
After tasks are delegated, it is possible to see how a particular person’s workload looks. You can reassign tasks if it seems that they have more than they can handle. It is perfect for anyone who may have taken on too much at once. Tracking their workload will ensure the person’s productivity. RACI can also reward people who have learned their tasks. They can be reassigned to new ventures that will help them develop while keeping them employed. It is an excellent motivator for those who have shown that they are ready to progress in the business.
Avoid workload and silos
Workload assessment does not have to fall entirely on the manager’s shoulders. Instead, the software keeps track of their workload, saving them time and maintaining a record. It is realistic for any company to have their best workers working at their highest level and delivering good results. All in need of assistance will obtain it, and those that shine will be remembered.
Set clear expectations
When you use the RACI to delegate positions and responsibilities, it’s quick to see who does what. People are often perplexed about how to play a different position, mainly if it is outside of their usual job title. Taking the time to outline what roles people play can reduce uncertainty and set clear expectations.
Effective method
RACI chart is an effective tool that saves the company’s time and money in the long run. New team members can easily catch up, and overall becomes a thing of the past. It is perfect for any organization that works on several projects at the same time. Team members understand what is required of them, and communication is much easier. It is simple to tell team members what to do, but if they are not following protocols, they can talk with a boss. It not only aids in project organization but also holds people responsible for their actions.
Encourage to take responsibility
To prevent delays, it is essential that any problems involving accountability be resolved as soon as possible. Encouraging team members to take responsibility would aid the company’s progress and completion of potential projects. Whatever needs to be done, fixing any problems would favor the organization in the long run.
Downloading and using a project RACI chart template that we are offering for free as an integrated part of your project planning program helps you remain organized and encourages your team members to connect quickly and efficiently, whether your organization is just starting out or consistently making the Fortune 500 list.
Professional Tips to Remember
Here are some tips and tricks to make your RACI Chart work perfectly :
Avoid generic or administrative to-dos- avoid generic or administrative to-dos like team meetings or status reports. If you have created a RACI chart, you are already covering up the generic and to-dos type of meeting and reports, so you don’t have to do that again.
Align the RACI chart tasks with that of your project plan- For the success of a RACI chart task in the chart must align with your overall project plan. Adding any unnecessary tasks will result in wastage of time and resources.
Keep RACI definitions close-by- Another essential tip for a RACI chart to work efficiently is to keep the definitions close-by not to have issues at the end of the project because you may forget them.
Be sure to assign the proper team members to the task- To make a RACI chart worthwhile, it is essential that you have a good team and you have assigned the right members the right task.
Make sure you understand the terms- Ensure that you understand the terms you are operating from a realistic position to make a RACI chart work for you.
The RACI model is an excellent method for evaluating and comprehending roles and obligations. However, several teams who use it do not find it to be as powerful as it should be. There are several different approaches to making project management more efficient. Some of the alternatives to the RACI matrix have been briefly discussed below:
RASCI
RASCI includes an extra option to mark people as that is the S.
The letter “S” stands for “Support,” and it is a form of participation that is like “Consult” in terms of the type of involvement, such as contributing information and services to a task/project but varies in the length of involvement and the end goals.
“Support” positions pursue task completion and remain involved participants during the task/project timeline. The Consultancy positions, on the other hand, have no such targets.
CARS
CARS is an acronym for
- Communicate
- Approve
- Responsible
- Support
When tasks are not completed by one role or person alone, CARS becomes more specific to actions and, much like RASCI, adds in the Support role. It clarifies other team members’ position as assisting with the mission rather than being the named person with ultimate responsibility.
RAS
It is an acronym for
- Responsible
- Approve
- Support
It does not, however, account for the task’s owner, which may lead to misunderstanding. It is a standard tool because it demonstrates what each team member is supposed to do ‘at a glance.’ Multiple resources can be connected to a task using scheduling tools like Microsoft Project, but there is no simple way to demonstrate what each resource is supposed to do. RAS fill the gap.
DACI
The acronym DACI stands for
- Driver (the individual who drives the decision)
- Accountable (the person who makes the decision)
- Contributors (the people or teams whose work or skills assist in the project)
- Informed (the people whose work might be affected by these decisions and who therefore need to be kept in the loop)
The DACI decision-making system is a model designed to increase a team’s productivity and velocity on projects by assigning tasks and responsibilities to team members regarding group decisions.
CLAM
CLAM is an acronym for
- Contributes
- Leads
- Approves
- Monitors
There is not much variation between CLAM matrix and RACI in terms of what the two are trying to achieve. It serves a similar process as that of the RACI matrix.
A RACI chart is useful across most of the projects, if not all.
No, there should be one and only one accountable for each task irrespective of the task’s nature. The reason for not having more than one account is that it creates a burden for an individual and affects productivity in the long run.
RACI chart is an easy-to-use visual tool that clearly defines each employee’s roles, roles, and responsibilities in the activities of a process. However, there are specific rules that can make the use of RACI efficient. The RACI matrix is an essential tool that can help implement and adequately function a process. This matrix is mainly used to align human elements within a process. There are usually many different people involved in a process, and each has different responsibilities. A RACI matrix then provides detailed documentation and maintains a reference ready to use at different stages of the process.
Looking For Document Management System?
Call Pursho @ 0731-6725516
Check PURSHO WRYTES Automatic Content Generator
https://wrytes.purshology.com/home
Telegram Group One Must Follow :
For Startups: https://t.me/daily_business_reads




